Deadlock Detection
In concurrent processing environments, a deadlock is an undesirable situation where two or more threads are mutually waiting for others to finish using some resources and cannot proceed further. Your task is to detect whether there is any possibility of deadlocks when multiple threads try to execute a given instruction sequence concurrently.
The instruction sequence consists of characters '
There are 10 shared resources called locks from L0 to L9.
A digit k is the instruction for acquiring the lock Lk.
After one of the threads acquires a lock Lk,
it is kept by the thread until it is released by the instruction '
Precisely speaking, the following steps are repeated until all threads finish.
- One thread that has not finished yet is chosen arbitrarily.
- The chosen thread tries to execute the next instruction that is not executed yet.
- If the next instruction is a digit k and the lock Lk is not kept by any thread, the thread executes the instruction k and acquires Lk.
- If the next instruction is a digit k and the lock Lk is already kept by some thread, the instruction k is not executed.
- If the next instruction is '
u ', the instruction is executed and all the locks currently kept by the thread are released.
After executing several steps, sometimes, it falls into the situation that the next instructions of all unfinished threads are for acquiring already kept locks. Once such a situation happens, no instruction will ever be executed no matter which thread is chosen. This situation is called a deadlock.
There are instruction sequences for which threads can never reach a deadlock regardless of the execution order. Such instruction sequences are called safe. Otherwise, in other words, if there exists one or more execution orders that lead to a deadlock, the execution sequence is called unsafe. Your task is to write a program that tells whether the given instruction sequence is safe or unsafe.
Input
The input consists of at most 50 datasets, each in the following format.
n
s
n is the length of the instruction sequence and s is a string representing the sequence.
n is a positive integer not exceeding 10,000.
Each character of s is either a digit ('
The end of the input is indicated by a line with a zero.
Output
For each dataset, if the given instruction sequence is safe, then print
Sample Input
11 01u12u0123u 6 01u10u 8 201u210u 9 01u12u20u 3 77u 12 9u8u845u954u 0
Output for the Sample Input
SAFE UNSAFE SAFE UNSAFE UNSAFE UNSAFE
The second input "
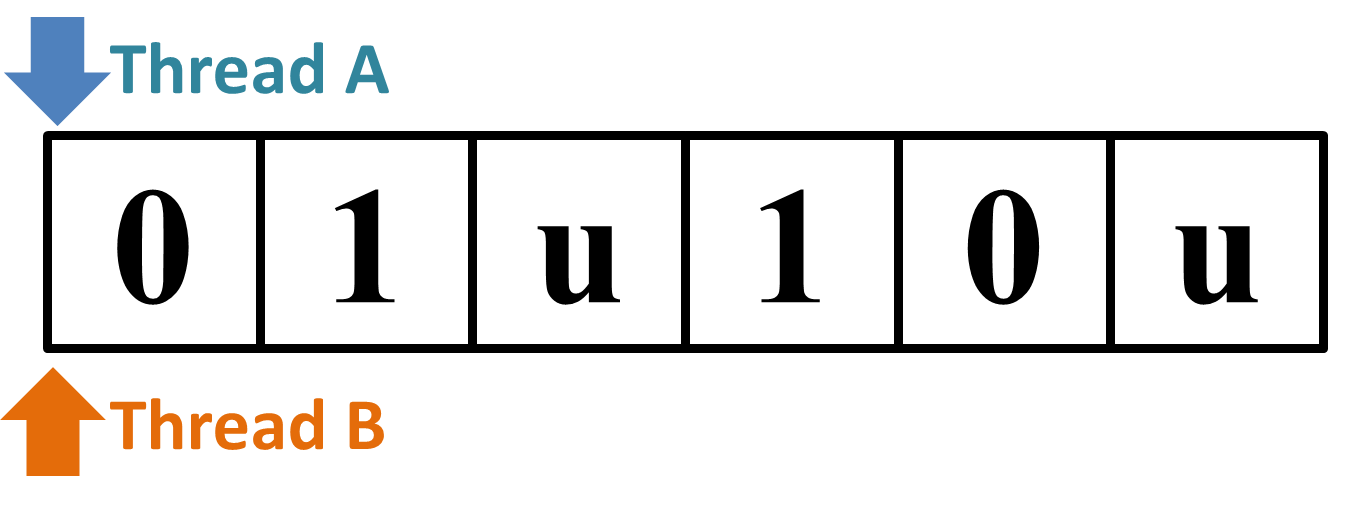 →
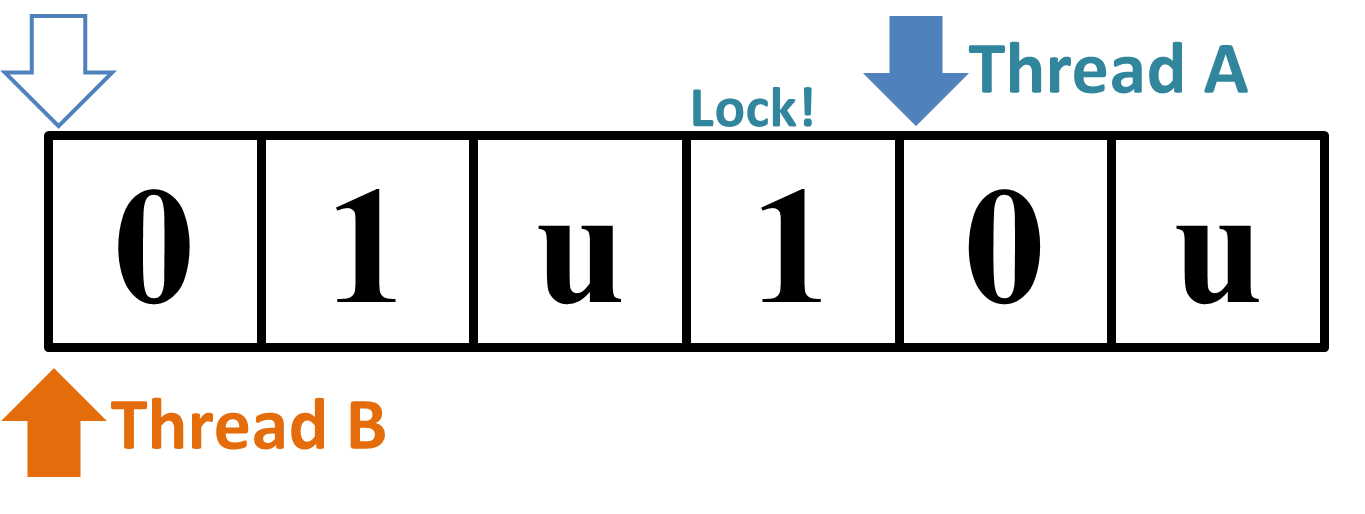
→
 →
→
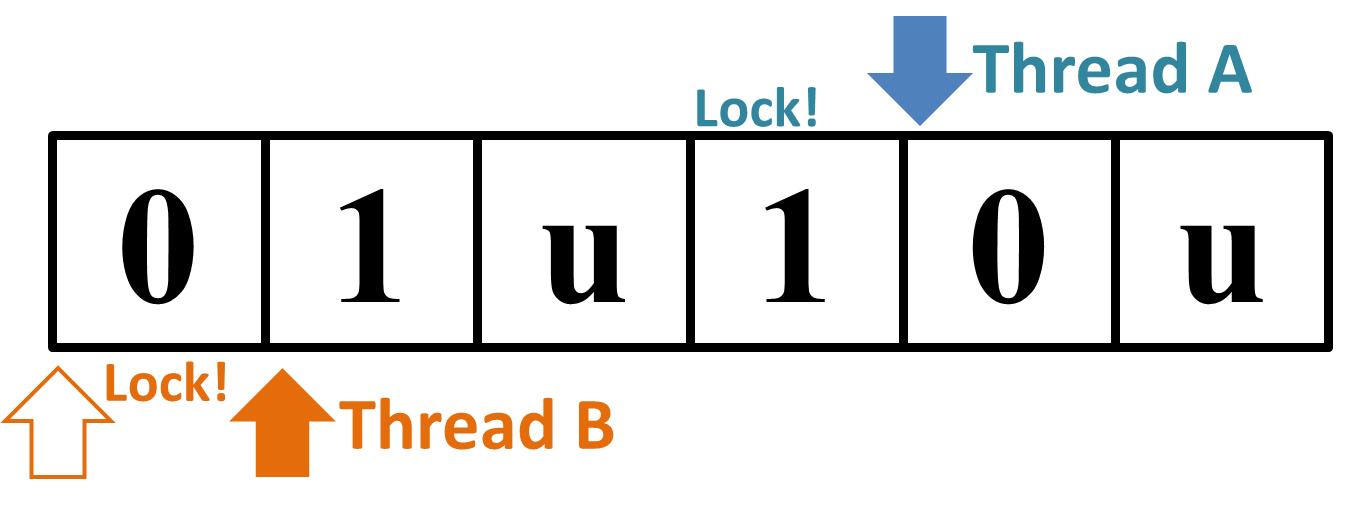
Figure 1: Why the Sample Input 2 "
Contrarily, the third input "